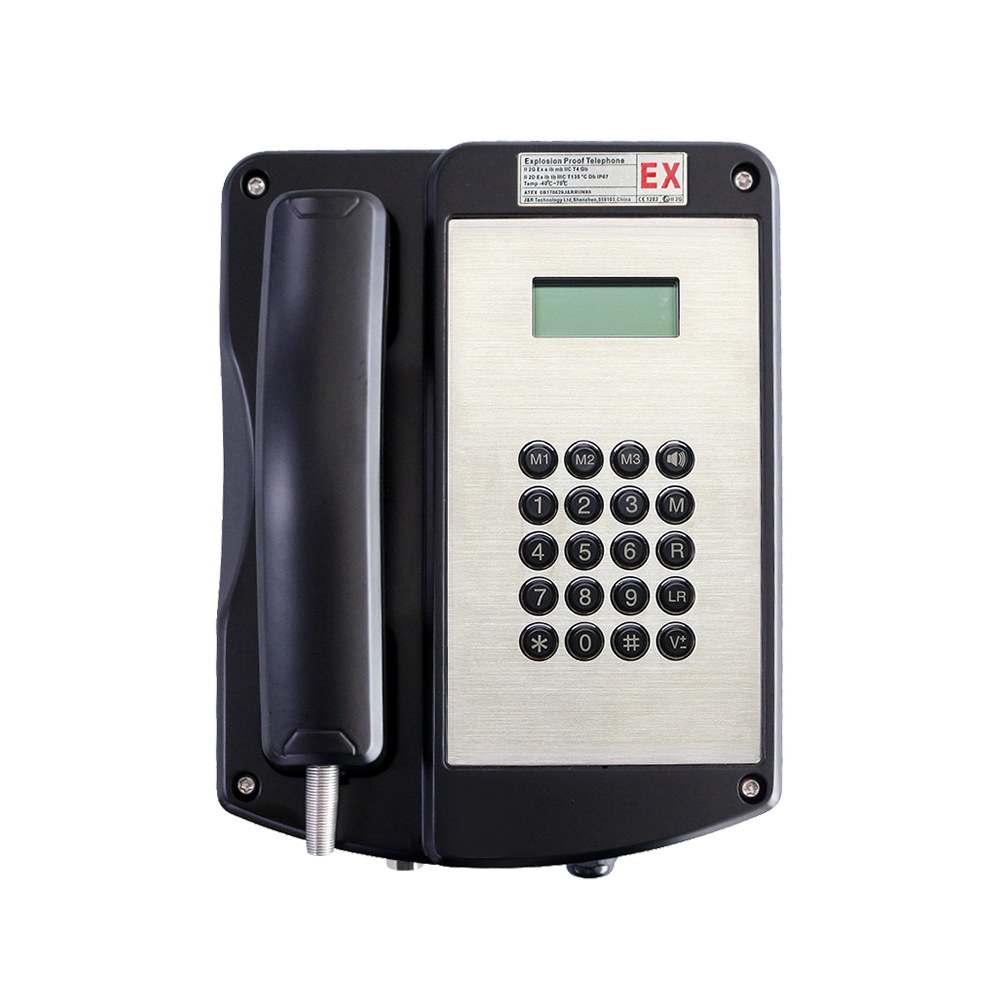
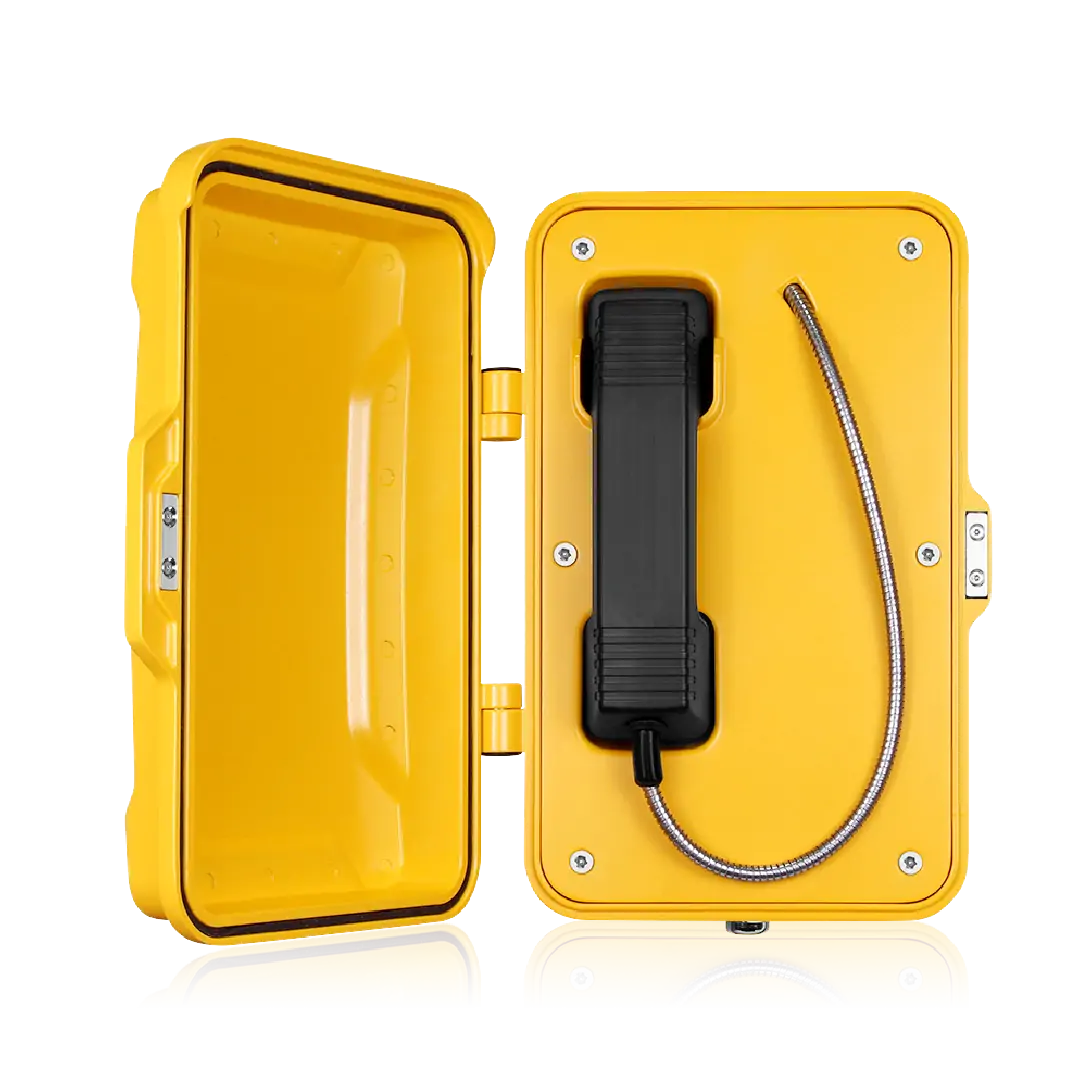
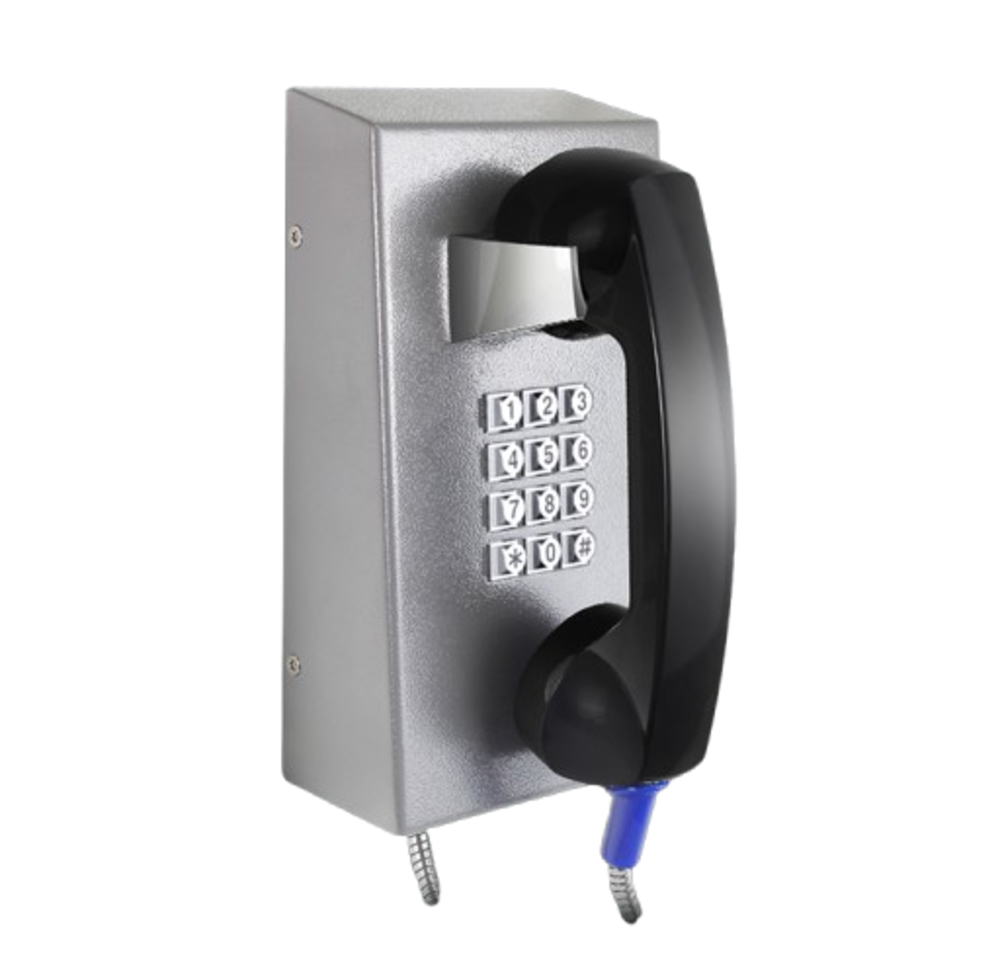
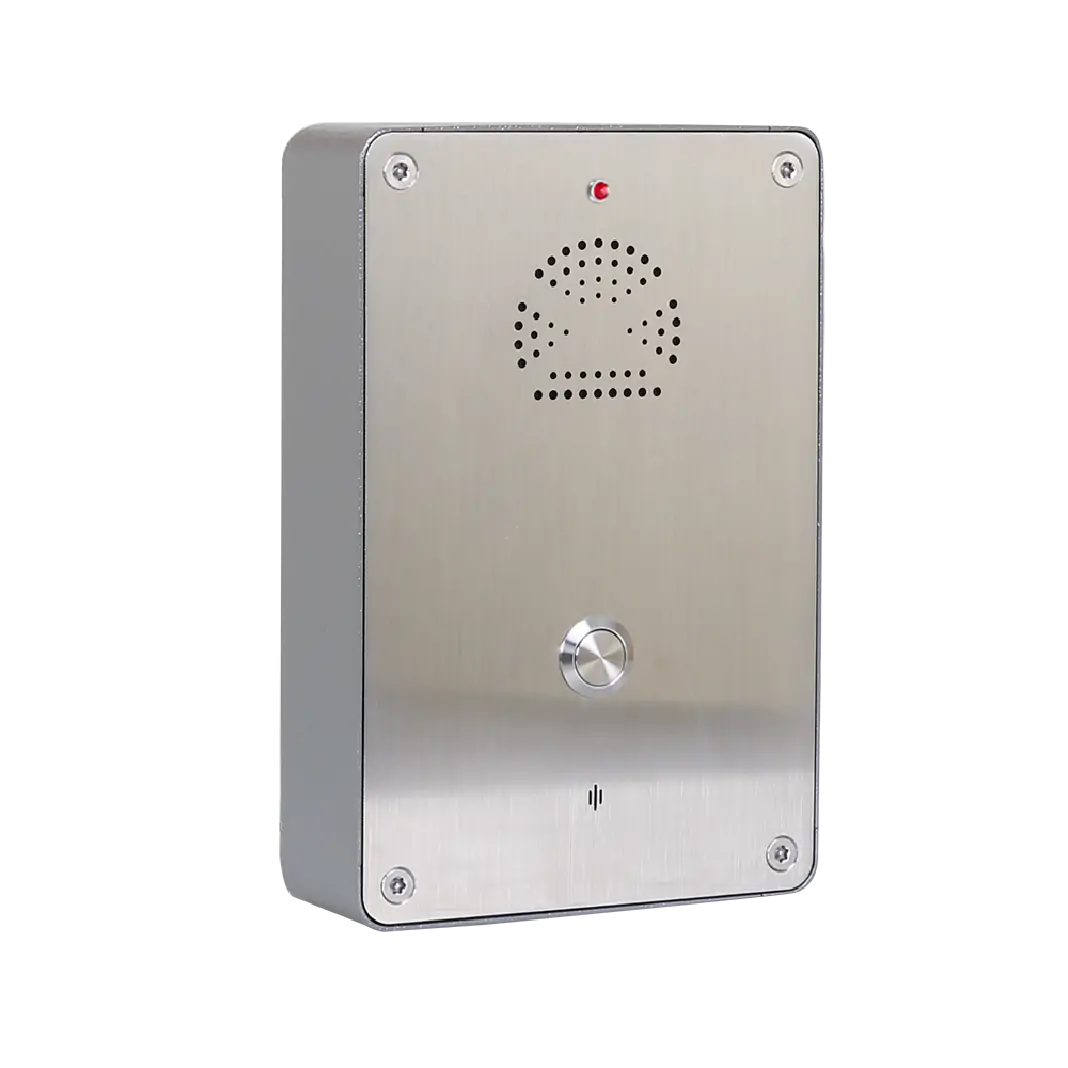
Secure and reliable communication is a fundamental requirement in prisons and correctional facilities. Unlike commercial or public environments, these facilities demand systems that can withstand abuse, prevent misuse, and integrate seamlessly with security infrastructure. Prison industrial telephones, often combined with acoustic hoods, have become a standard solution to support controlled inmate communication while maintaining institutional safety, compliance, and operational efficiency.
This article explores how industrial telephones and acoustic hoods are applied in correctional environments, why they are essential, and how they meet strict correctional standards worldwide.

Why Do Prisons Require Specialized Communication Systems?
Correctional facilities operate under unique constraints: high noise levels, constant supervision, and elevated risks of vandalism or tampering. Conventional commercial telephones are not designed to survive these conditions or comply with correctional security policies.
Prisons require communication systems that:
-
Allow inmates to maintain approved contact with family, legal counsel, and staff
-
Enable monitoring, call control, and recording to prevent prohibited activity
-
Withstand frequent use, intentional abuse, and harsh environmental conditions
-
Integrate with centralized security platforms such as control rooms, alarms, and access systems
As a result, prison industrial telephones are purpose-built to balance humane communication needs with uncompromising security requirements.
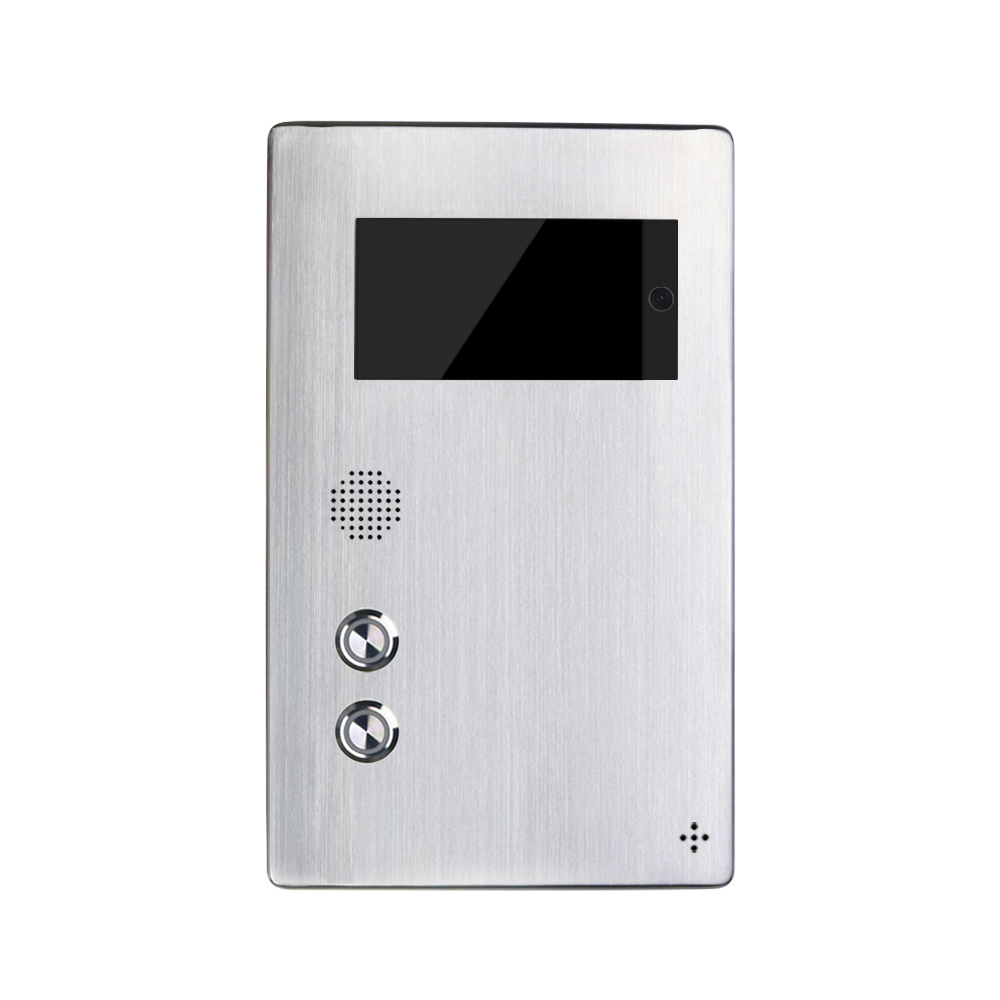
What Makes Industrial Telephones Suitable for High-Security Facilities?
Industrial telephones used in prisons are fundamentally different from standard telephony equipment. Their design prioritizes durability, security, and system integration.
Key characteristics include:
Vandal-resistant construction
These telephones are typically manufactured from heavy-duty materials such as cold-rolled steel or stainless steel. Features like armored handset cords, metal keypads, and tamper-proof fasteners prevent damage, dismantling, or weaponization.
Controlled and monitored communication
Calls can be routed through secure platforms that enable recording, monitoring, call-time limits, and approved contact lists. This ensures compliance with institutional policies while maintaining transparency and accountability.
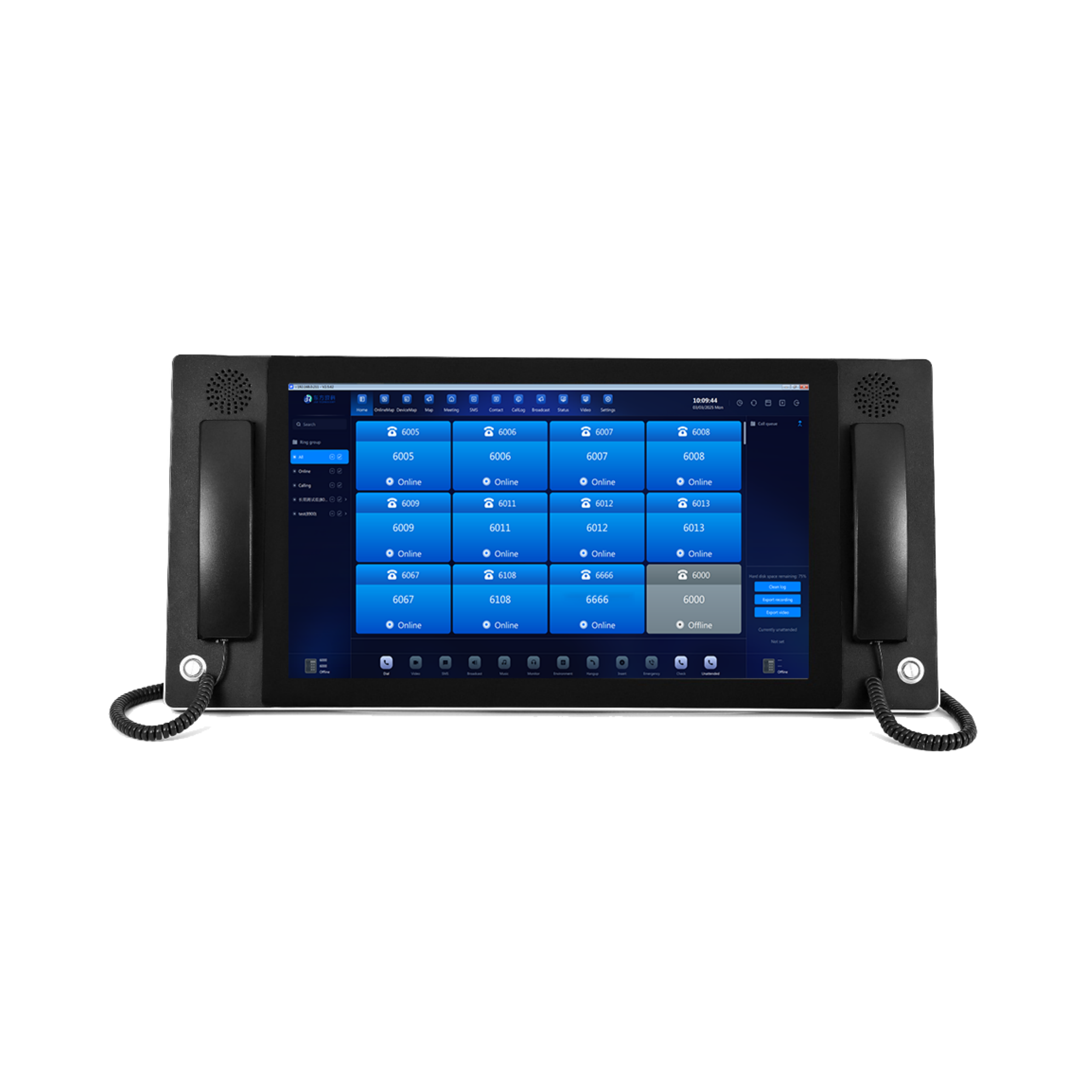
System integration capabilities
Modern industrial telephones support SIP or VoIP protocols, allowing integration with:
-
Control room dispatch systems
-
CCTV and access control platforms
-
Emergency alarm and public address systems
-
Video intercom solutions for identity verification and supervised interaction
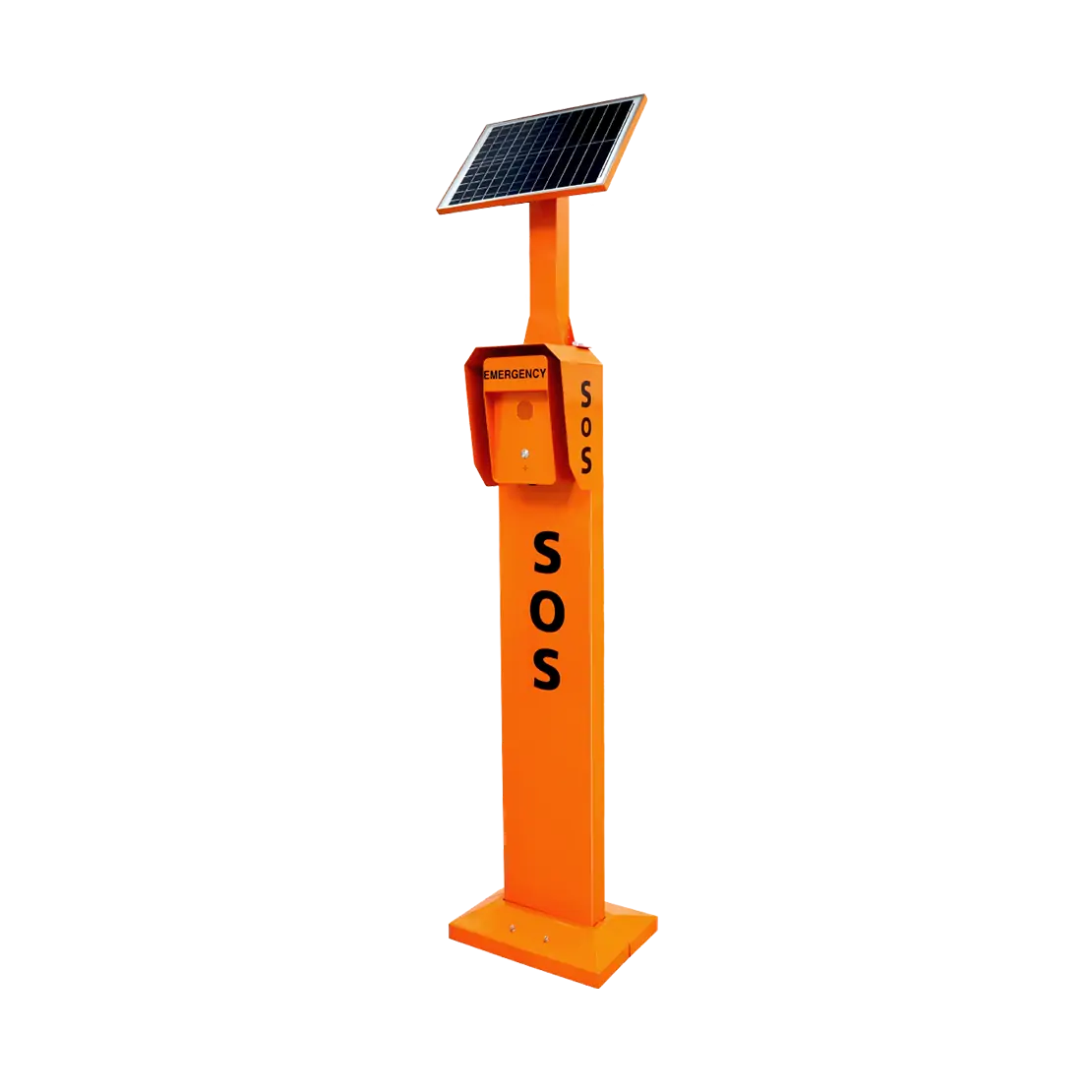
Hands-free and emergency functionality
Hands-free operation, speed dialing, and emergency call buttons allow rapid communication in high-risk situations, protecting both inmates and correctional staff.
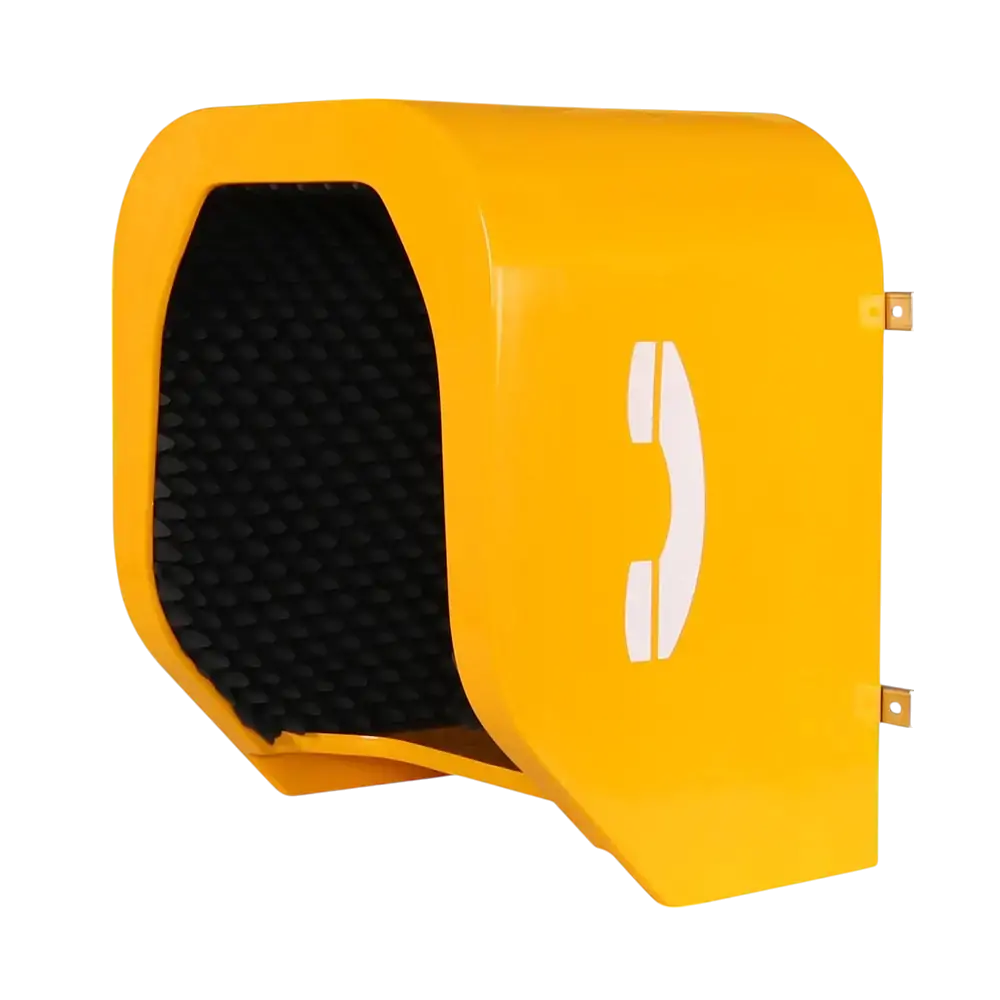
How Do Acoustic Hoods Improve Privacy and Noise Control?
Correctional facilities are acoustically challenging environments. Hard surfaces, metal structures, and constant activity generate high reverberation and background noise, which can compromise call clarity and increase stress levels.
Acoustic hoods are engineered to address these challenges by creating localized sound-controlled zones.
Noise reduction and call clarity
Sound-absorbing linings significantly reduce ambient noise and echo, ensuring clearer communication for both inmates and monitoring officers.
Improved privacy without compromising security
While calls remain monitored and controlled, acoustic hoods limit sound leakage into surrounding areas. This reduces tension between inmates and improves overall facility order.
Robust, abuse-resistant materials
Acoustic hoods used in prisons are typically constructed from GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic), steel, or composite materials designed to resist impact, fire, and chemical exposure.
Visual safety and signaling options
Many acoustic hoods can be equipped with LED indicators or beacons, allowing staff to visually monitor usage status or identify emergency calls instantly.
Where Are These Systems Installed Within Prisons?
Industrial telephones and acoustic hoods are deployed strategically across correctional facilities to support both routine and emergency communication.
Common installation areas include:
-
Cell blocks and housing units for scheduled inmate calls
-
Visitation areas to supplement supervised contact
-
Corridors and common areas for emergency communication
-
Workshops, yards, and recreational zones where noise levels are high
-
Segregation or high-security units requiring hands-free or restricted-access communication
In many cases, telephones are mounted within acoustic hoods to create a dedicated, durable, and controlled calling station that minimizes environmental impact.
How Do These Communication Systems Meet Correctional Standards?
Correctional communication equipment must comply with strict regulatory and operational standards. Industrial telephones and acoustic hoods are engineered with these requirements in mind.
Compliance and durability ratings
High IK rating performance ensures resistance to mechanical impact and vandalism. Enclosures are often rated for ingress protection to withstand dust, moisture, and cleaning procedures.
Safety and operational reliability
Fire-resistant materials, anti-ligature designs, and sealed electronics reduce risk and ensure continuous operation in demanding environments.
Centralized management and scalability
Integration with prison management systems allows administrators to:
-
Control call permissions and durations
-
Monitor system health remotely
-
Expand or reconfigure communication points as facilities evolve
Support for modern correctional strategies
By improving call quality and reducing noise-related stress, these systems contribute to safer environments, better staff-inmate interactions, and compliance with international correctional facility guidelines.
Conclusion
In modern correctional facilities, communication is not merely a convenience—it is a controlled, security-critical function. Prison industrial telephones, when combined with durable acoustic hoods, provide a proven solution that balances inmate communication rights with institutional safety and operational control.
By offering vandal resistance, monitored communication, noise reduction, and seamless integration with broader security systems, these solutions play a vital role in creating safer, more efficient correctional environments.
As correctional infrastructure continues to modernize, industrial communication systems will remain a core component of secure facility design worldwide.
 Petrochemical FacilitiesDetails
Petrochemical FacilitiesDetails Offshore Oil Drilling PlatformsDetails
Offshore Oil Drilling PlatformsDetails Onshore Oil PlatformsDetails
Onshore Oil PlatformsDetails Industrial & Manufacturing FacilitiesDetails
Industrial & Manufacturing FacilitiesDetails Nuclear Power PlantsDetails
Nuclear Power PlantsDetails Mining Communication SystemsDetails
Mining Communication SystemsDetails Expressways & HighwaysDetails
Expressways & HighwaysDetails Utility TunnelsDetails
Utility TunnelsDetails Heavy Machinery Zones (Cranes)Details
Heavy Machinery Zones (Cranes)Details Pharmaceutical Plants & CleanroomsDetails
Pharmaceutical Plants & CleanroomsDetails Correctional FacilitiesDetails
Correctional FacilitiesDetails Healthcare & Campus FacilitiesDetails
Healthcare & Campus FacilitiesDetails Smart CitiesDetails
Smart CitiesDetails 4G Communication SolutionsDetails
4G Communication SolutionsDetails Wind Power PlantsDetails
Wind Power PlantsDetails










































