In modern manufacturing environments, emergency preparedness is no longer optional—it is a core operational requirement. From large-scale production lines and automated workshops to hazardous material storage and utilities infrastructure, manufacturing plants face complex risks that demand fast, reliable, and coordinated communication. As a result, emergency communication systems for manufacturing plants have become a critical investment for plant operators worldwide.
This article reviews how emergency communication systems are evaluated, the main system categories available, key vendor considerations, real-world deployment examples, and the return on investment (ROI) manufacturers can expect.

Rating Criteria
Not all emergency communication systems are equal. Top-rated solutions are typically assessed against a combination of technical, operational, and compliance-driven criteria.
Reliability and availability
In an emergency, system failure is unacceptable. Highly rated systems are designed for 24/7 operation, often with redundant power supplies, failover communication paths, and industrial-grade components.
Environmental durability
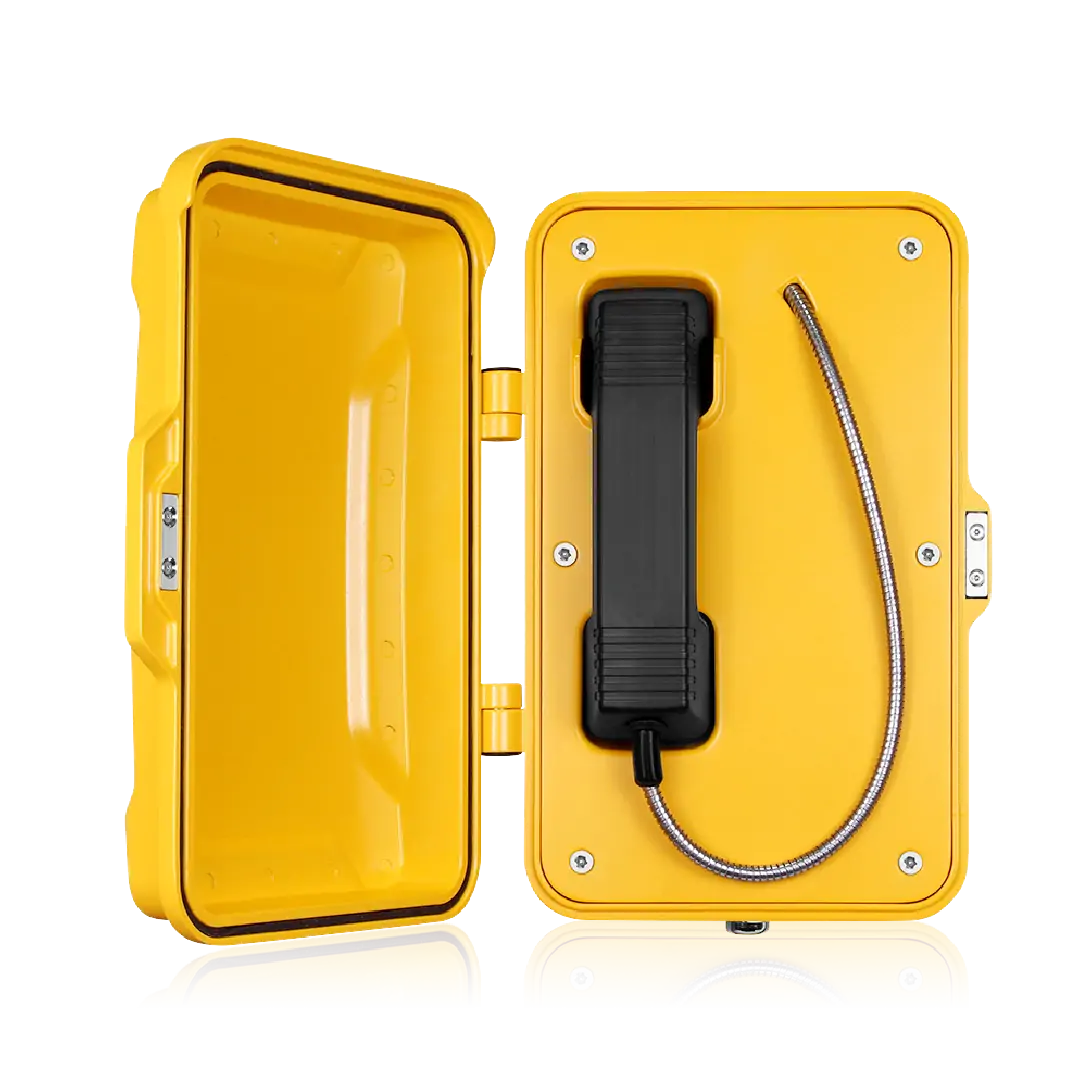
Manufacturing plants may expose equipment to dust, moisture, vibration, temperature extremes, and corrosive substances. Systems must meet industrial protection standards such as high IP and IK ratings.
Response speed and clarity
Emergency alerts must be delivered instantly and understood clearly. This includes intelligible voice communication, visible indicators, and prioritized signaling aligned with comm systems priority strategies.
Integration capability
Leading systems integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure, including SCADA, fire alarms, access control, and plant-wide PA systems, enabling coordinated emergency response.
Compliance and scalability
Compliance with local and international safety standards is essential. Systems should also be scalable, allowing plants to expand communication coverage as operations grow.
System Categories
Emergency communication systems for manufacturing plants typically fall into several core categories, often deployed together as part of an integrated safety solution.
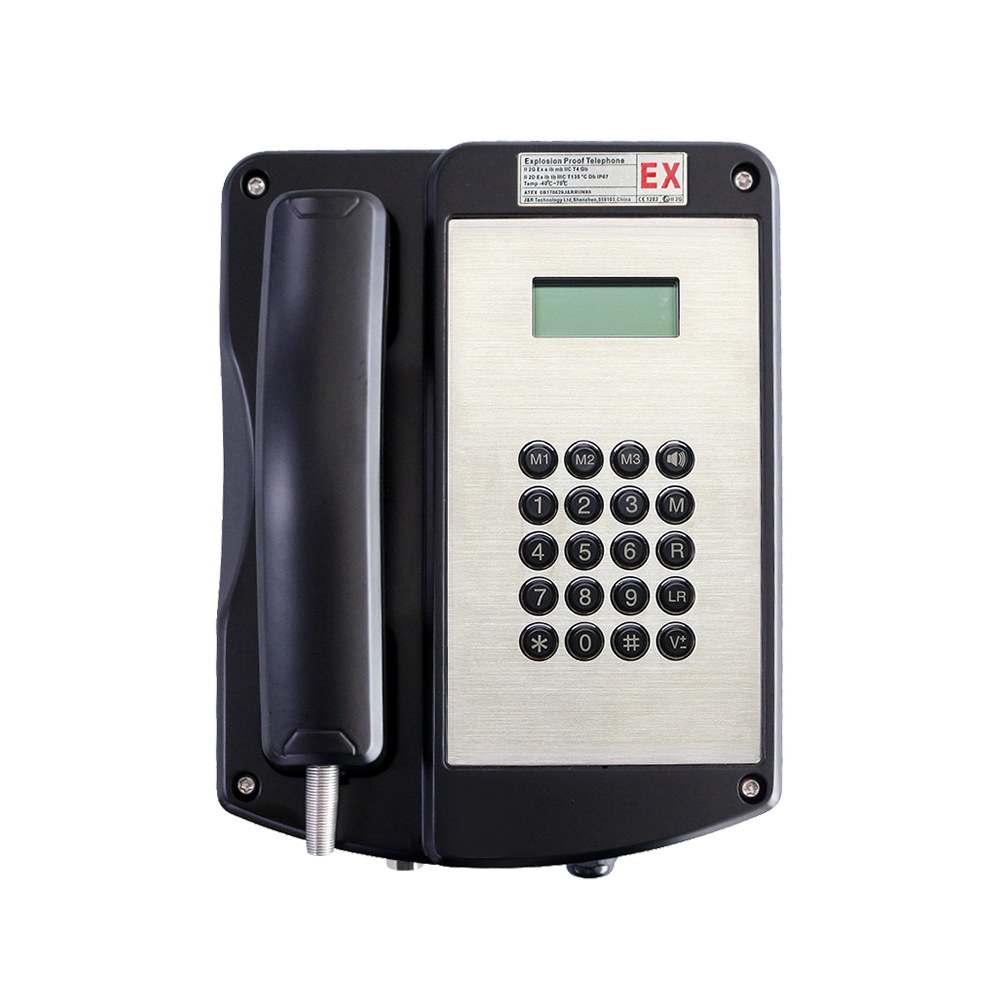
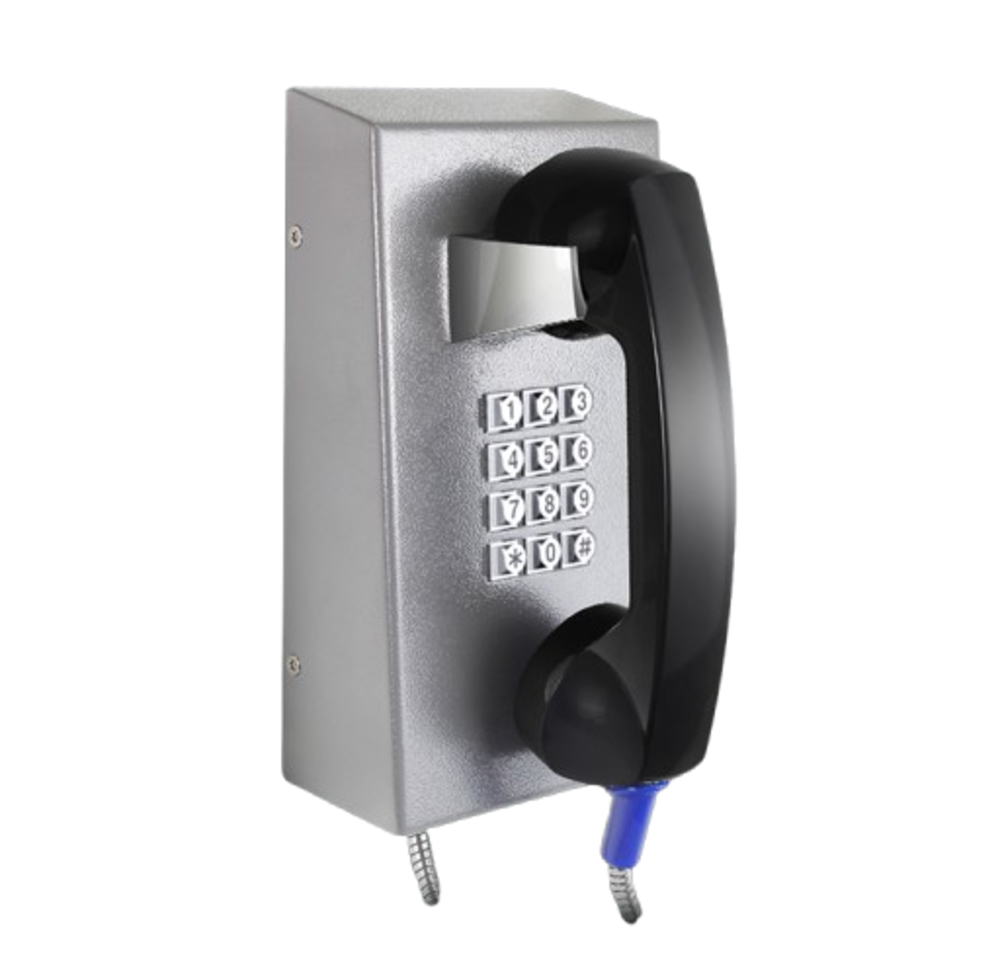
Industrial emergency telephones
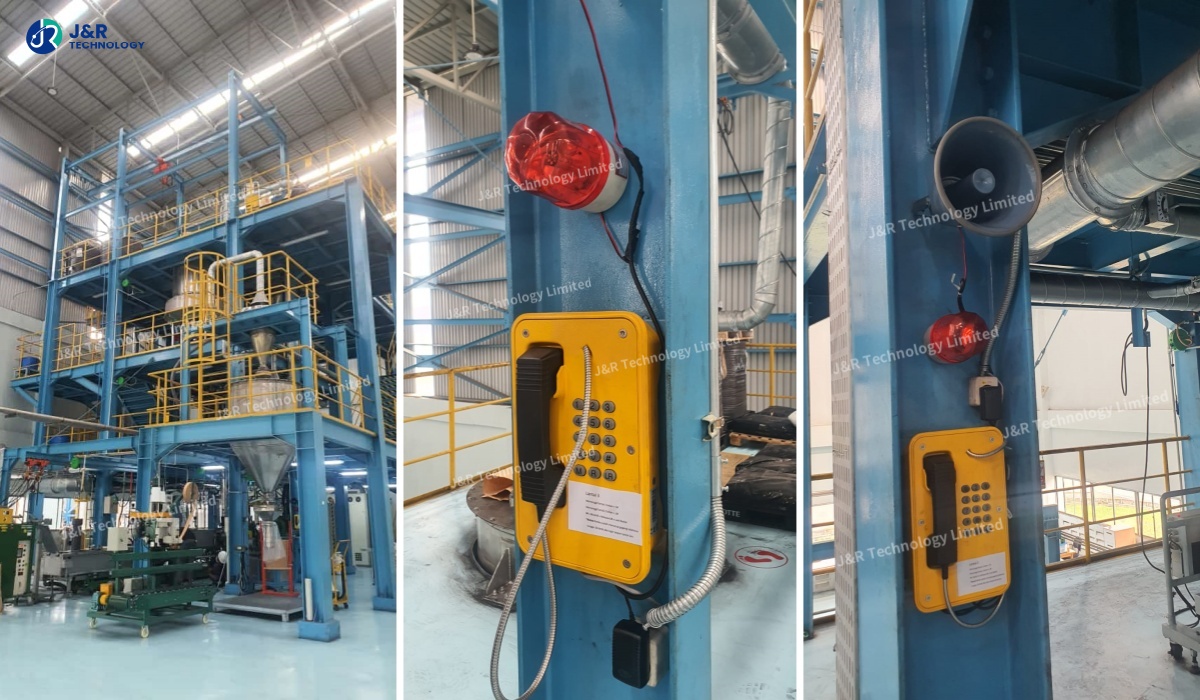
These rugged telephones provide direct, reliable voice communication between workers and control rooms during incidents. They are commonly installed in production areas, warehouses, tunnels, and outdoor zones.
Public Address and Voice Alarm (PA/VA) systems
PA/VA systems enable centralized or zoned emergency announcements, guiding personnel during evacuations, equipment failures, or hazardous releases.
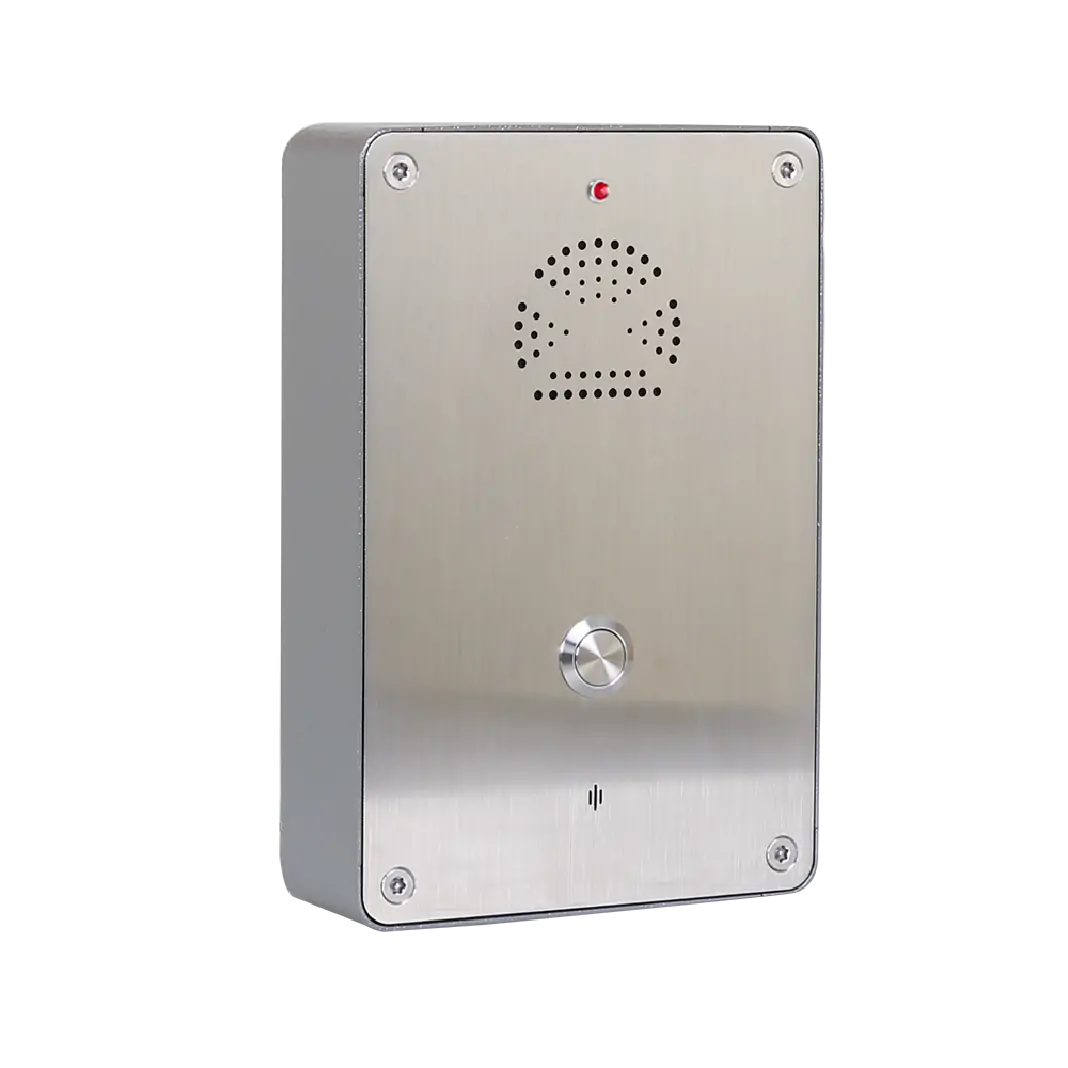
Industrial intercom and video intercom systems
Intercom solutions allow two-way communication at access points, production lines, and control stations. Video intercoms add visual verification, enhancing situational awareness.
Visual and audible alarm devices
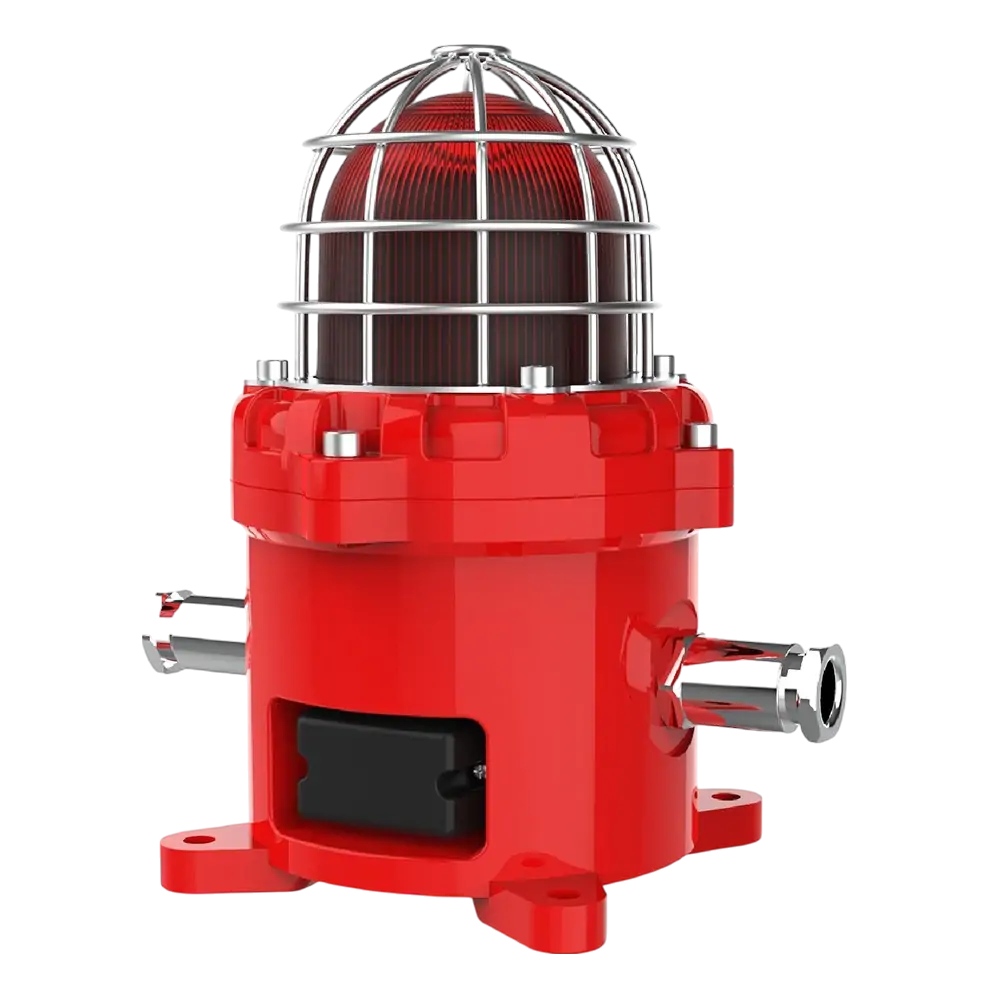
Beacons, sirens, and LED indicators provide immediate non-verbal alerts, particularly useful in high-noise manufacturing environments.
Integrated IP-based communication platforms
Modern plants increasingly adopt IP-based systems that unify voice, video, alarms, and data, supporting remote monitoring and centralized management across multiple facilities.
Vendor Comparisons
When comparing vendors, manufacturers should look beyond brand recognition and focus on system suitability for industrial conditions.
Industrial specialization
Top-rated vendors design communication systems specifically for heavy industry, rather than adapting commercial products. This ensures higher durability and compliance.
Customization and system engineering
Manufacturing plants vary widely by industry—automotive, chemical, food processing, or heavy machinery. Leading suppliers offer configurable solutions tailored to plant layouts and risk profiles.
Integration with hazardous environments
For facilities handling flammable gases or chemicals, compatibility with hazardous-area requirements and oil gas connectivity principles is a strong indicator of technical maturity.
Global support and lifecycle service
Multinational manufacturers benefit from vendors with global technical support, long product lifecycles, and spare-part availability.
Cybersecurity and network resilience
As IP-based systems become standard, secure architecture and network resilience are increasingly important evaluation factors.
Deployment Examples
Real-world deployments demonstrate how emergency communication systems function in diverse manufacturing scenarios.
Automotive manufacturing plants
Emergency telephones and PA systems are installed along assembly lines and logistics zones, enabling rapid incident reporting and coordinated evacuation during equipment failures.
Chemical and pharmaceutical facilities
Explosion-resistant emergency communication devices are deployed in hazardous zones, integrated with gas detection and fire alarm systems for immediate response.
Steel and heavy industry plants
Rugged intercoms and high-output loudspeakers support communication across vast, noisy environments, ensuring instructions remain audible during emergencies.
Food and beverage production
Hygienic, sealed communication devices are used in processing areas, supporting safety compliance while maintaining operational continuity.
In each case, the effectiveness of the system depends on thoughtful design, proper zoning, and integration with broader safety infrastructure.
ROI Analysis
While emergency communication systems are often viewed as a compliance cost, their return on investment is substantial and measurable.
Reduced incident impact
Faster communication minimizes downtime, equipment damage, and injury severity during emergencies.
Improved workforce safety and confidence
Clear, reliable communication improves worker confidence and adherence to safety procedures, reducing accident frequency over time.
Regulatory compliance and risk mitigation
Meeting safety regulations helps manufacturers avoid fines, legal exposure, and reputational damage.
Operational efficiency beyond emergencies
Many systems support daily operational communication, maintenance coordination, and security management, extending their value beyond crisis situations.
Long-term cost savings
Industrial-grade systems offer long service life and lower replacement costs compared to commercial alternatives, improving total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
Selecting the right emergency communication systems for manufacturing plants is a strategic decision that directly impacts safety, compliance, and operational resilience. Top-rated systems excel in reliability, durability, integration, and scalability, while supporting clear communication under the most demanding conditions.
As manufacturing plants continue to modernize and digitize, emergency communication will remain a foundational element of industrial safety architecture—protecting people, assets, and business continuity in equal measure.
 Petrochemical FacilitiesDetails
Petrochemical FacilitiesDetails Offshore Oil Drilling PlatformsDetails
Offshore Oil Drilling PlatformsDetails Onshore Oil PlatformsDetails
Onshore Oil PlatformsDetails Industrial & Manufacturing FacilitiesDetails
Industrial & Manufacturing FacilitiesDetails Nuclear Power PlantsDetails
Nuclear Power PlantsDetails Mining Communication SystemsDetails
Mining Communication SystemsDetails Expressways & HighwaysDetails
Expressways & HighwaysDetails Utility TunnelsDetails
Utility TunnelsDetails Heavy Machinery Zones (Cranes)Details
Heavy Machinery Zones (Cranes)Details Pharmaceutical Plants & CleanroomsDetails
Pharmaceutical Plants & CleanroomsDetails Correctional FacilitiesDetails
Correctional FacilitiesDetails Healthcare & Campus FacilitiesDetails
Healthcare & Campus FacilitiesDetails Smart CitiesDetails
Smart CitiesDetails 4G Communication SolutionsDetails
4G Communication SolutionsDetails Wind Power PlantsDetails
Wind Power PlantsDetails










































